At the two conferences in 2015, the word "big data" was first written into the government work report. In the area of ​​transportation, big data has always been regarded as a technological weapon to ease traffic pressure. The application of big data helps to understand the rules and causes of people's travel in urban traffic congestion problems, realize the harmony of traffic and life, improve the livability of cities, and provide comprehensive decision-making based on data evidence for the precise management of the government. At the same time, the mining and use of big data is also conducive to creating a new model of information consumption and promoting the development of information consumption industries.
With the development of the mobile phone network, global positioning system (GPS)/BeiDou in-vehicle navigation, car networking, and transportation internet of things, information on people, vehicles, and roads of the transportation elements can be collected in real time. Increasingly rich. With the help of the increasingly sophisticated Internet of Things and cloud computing platforms, through the collection, transmission, storage, mining, and analysis of urban traffic big data, it is expected to realize the integration of urban transportation, that is, to realize traffic administrative supervision and transportation enterprises on a platform. Operations, transportation, citizen service integration and optimization.
The research on integration and analysis of urban traffic big data has strategic significance for the development of smart cities in China. Traffic big data has a wide range of characteristics, heterogeneity, large spatial and temporal scales, dynamic changes, high randomness, locality and limited life cycle characteristics, how to effectively integrate traffic big data, meet the timeliness and knowledge traction and other cities The demand for smart transportation is an unprecedented development opportunity and challenge faced by large and medium-sized cities.
This article first briefly introduced the development status and trends of big data, and then focused on analyzing and summarizing some core technologies of urban traffic big data, and proposed an intelligent application system solution for urban traffic big data, and finally listed several typical applications.
2 Big Data Development and Trends
In recent years, the rapid growth of data has become a serious challenge and a valuable opportunity faced by many industries. The information society is entering the era of big data. Big data refers to the huge amount of data involved so that it can't reach the data collection of perception, retrieval, management, processing and services within a reasonable time through the current mainstream software tools. Since about 2009, "big data" has become a popular vocabulary in the Internet information technology industry.
According to estimates by the Internet Data Center (IDC), data has been growing at an annual rate of 50% (Moore’s Law of Big Data), which means that the amount of data generated by humans in the last two years is equivalent to the amount of data previously generated, and it is estimated that by 2020 In a year, the world will have a total of 3.5 billion GB (35 ZB) of data. The data size of big data processing has risen from terabytes to PB, EB, and even ZB. People are faced with many challenges, such as how to reduce data storage costs, make full use of computing resources, increase system concurrent throughput, and support distributed non-linear iterative algorithm optimization.
In order to respond to the development trend of big data and provide data analysis services for industry users and individuals, it is urgent to build various types of big data platforms to support users' multiple demands for data. To build a big data platform is to organically integrate data from different sources, different sources, and different structures. Different from traditional data platforms, the large-scale large-scale data, various types, rapid flow and dynamic system, and huge value are several factors that need to be considered in the construction of big data platforms. In addition, the classification and storage of data, the openness of data platforms, the intelligent processing of data, and the interaction of data platforms and users have brought unprecedented challenges to the construction of big data platforms.
The data types handled by big data platforms are varied. At present, the establishment of these platforms has achieved some representative results, such as Google's Freebase, Microsoft's Probase, and the well-known Chinese information structure database, China Knowledge Network. In terms of commercial data platforms, IBM’s Infosphere big data analysis platform, Teradata’s unified data environment from Tianrui, and China’s first e-commerce cloud work platform in China, jointly launched by domestic Tmall, Alibaba Cloud, and Wanwang, are three Typical data platform.
"Big data" itself is a phenomenon and not just a technology. This is the inevitable result of the historical development of information technology. The big data processing technology required for the collection, transmission, processing, and application of big data is the use of non-traditional tools to process a large amount of structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data to obtain analysis and prediction. The result of a series of big data processing techniques. The strategic significance of big data technology also lies not only in the mastery of huge data information, but also in the specialization of these meaningful data. In other words, if you compare big data to a single industry, the key to profitability of such industries is to improve the "processing power" of data and achieve "value-added" data through "processing." In the field of big data, a large number of new technologies have emerged. They have become powerful weapons for acquiring, storing, processing, and presenting big data. Big data development presents the following trends.
(1) Cloud-based data analysis platform
Cloud computing provides scalable, relatively inexpensive storage space and computing resources for big data, enabling small and medium enterprises to complete big data analysis through cloud computing just like Amazon. Cloud computing IT resources are huge and distributed widely. It is a powerful way or even the only way for enterprises with heterogeneous systems to process data in a timely and accurate manner.
In order to move toward cloud computing, big data also depends on the improvement of data communication bandwidth and the construction of a cloud resource pool. It is necessary to ensure that the original data can be migrated to the cloud computing environment and that the resource pool can be flexibly extended on demand.
(2) The data analysis set will gradually expand, and the enterprise-level data warehouse will become the mainstream
When people taste the sweetness from big data analysis, the data analysis set will gradually expand. At present, the amount of data analyzed by most companies is generally TB. According to the current speed of data development, the amount of data will soon enter the era of PB. In particular, the number of analytical data sets currently in the range of 100 to 500 TB and 500+ TB will increase exponentially.
With the expansion of data analysis sets, previous department-level data sets will not be able to meet the needs of big data analytics. They will become a subset of enterprise-level databases (EDWs). Therefore, the data analysis in the enterprise will shift from the department level to the enterprise level, and from department-oriented demand to business-oriented demand, and thus will also gain greater benefits than the department perspective. With the opening of government and industry data, more external data will enter the enterprise-level data warehouse, making the data warehouse larger and the data more valuable.
(3) Hadoop has become less dependent on MapReduce
Hadoop is a software framework capable of distributed processing of large amounts of data. It can process PB-level data and has features such as high reliability, high scalability, high efficiency, and high fault tolerance. The new version is not only for MapReduce services, but with Cloudera's Impala, using an SQL query engine or other methods instead of MapReduce. The HBaseNoSQL database is a good example of Hadoop's departure from MapReduce constraints. The future Hadoop platform will play an increasingly important role in big data processing.
3 City Traffic Big Data
  3.1 Main Research Contents of Urban Traffic Big Data
(1) Time-constrained big data multi-scale convergence calculation and dynamic graph
Traffic big data has the characteristics of multi-sources, heterogeneity, locality, spatio-temporal correlation, asynchrony, information sparsity, and concurrency, while the urban transportation system has a high timeliness for large data aggregation and processing, as well as “big and sparse informationâ€. "Traffic requirements for large areas of traffic knowledge traction. Existing data fusion and computational theory and methods are difficult to meet the needs of large time-consuming big data processing and data-based knowledge construction and conversion. It is urgent to propose time-constrained large-scale multi-scale convergence calculations and dynamic graphs for traffic big data processing. New theory and new method.
(2) Recessive knowledge sequential mining and evolution model in high-dimensional space
The traffic subject, behavior, situation, road network topology and environment form the closed space of the high-dimensional ecosystem, and there is a highly nonlinear, random and dynamic coupling relationship between them. The traffic situation and its evolution are the macroscopic manifestation of the traffic system, with the characteristics of dynamicity, sequence, self-organization, and randomness under constraints, and the interpretation of the traffic situation mechanism is very important for solving the problems of urban traffic. Traditional transportation theories can hardly find the knowledge implied in such a high-dimensional space. It explains and evaluates the comprehensive knowledge and data support for the law of traffic and its spatial and temporal evolution, the evolution law of large-area traffic congestion, and the environment and traffic behavior. The sequential mining and evolution of spatial tacit knowledge will provide a solid theoretical and technical support for this.
(3) Prediction mechanism and regulation strategy of traffic situation
The traffic situation is a reflection of the operating status of the urban traffic system and is influenced and influenced by many factors such as traffic demand, network topology, multiple traffic subsystems, environment, management, and regulatory strategies. Because of the characteristics of time-varying, uncertainty, non-Martensitic, and influencing factors, the urban traffic situation is an ultra-dimensional, complex, giant system whose regulation and prediction is a worldwide problem. Currently, there is a lack of correlation. Theories and methods. Research on the prediction mechanism and regulation strategy of traffic situation will create new theories and approaches for the prediction and control of complex traffic giants.
3.2 Urban Traffic Big Data Related Processing Technology
In the process of vigorous development of urban transport, the amount of data collected will inevitably grow exponentially, forming massive, dynamic and real-time traffic big data. Therefore, the urban traffic information service supported by big data processing technology will become the growth point of intelligent traffic development in the future. The big data technologies involved in urban transportation are summarized as follows.
(1) MapReduce mode technology based on Hadoop framework
Hadoop is a software framework capable of distributed processing of large amounts of data, and map/reduce is the core computing model of Hadoop. It parallelizes two functions in a highly parallel computing process that runs complexly on large-scale clusters. Hadoop implements a distributed file system (HDFS). HDFS is highly fault-tolerant and is designed to be deployed on inexpensive hardware. And it can provide high transfer rate to access application data, suitable for those applications with large data sets.
(2) Data Warehouse Technology
Data warehousing is a structured data environment for decision support system (DSS) and online analytical application data sources. It studies and solves issues such as obtaining information from databases. Data warehouses are characterized by topic-oriented, integrated, stability, and time-varying. Its main function is to organize and analyze the organization's online data processing (OLTP) of the information system over a large number of years and data storage structures unique to the data warehouse theory to facilitate various analysis methods such as online analysis and processing ( OLAP and data mining are used to support the creation of systems such as decision support systems and executive information systems (EIS). This helps decision makers to quickly and effectively analyze valuable information from large amounts of data to facilitate Make decisions and quickly respond to changes in the external environment to help build business intelligence.
(3) Central Data Register Technology
The central data registry system is the basis for unified management and comprehensive traffic information services for platform data, including data representation and interaction related to traffic information and traffic information services, data dictionary and message templates suitable for integrated traffic environment, and traffic data item definition rules. , registration and management mechanisms, etc.
(4) Platform GIS-T application technology
The platform GIS-T application technology is the supporting technology of the transportation geographic information system, which can provide efficient information query functions and massive storage functions for traffic information services, including taxi, bus, comprehensive traffic video information, etc.; providing excellent user experience The WebGIS engine allows users to enjoy browser-based traffic information services.
(5) Non-sequential data manipulation techniques
Non-sequential data manipulation technologies, including virtualized environments and streaming data processing technologies, integrate a large number of server memory spaces through a network to form a very large virtual memory, and then perform data configuration on it to achieve The maximum use efficiency of existing equipment resources, and the ability to feed back real-time data at the same time.
(6) Video Big Data Processing Technology
The video big data processing technology integrates all current specialized video surveillance systems organically to achieve the “five-unified†goal of unified video resource access, unified transcoding, unified distribution, unified management, and unified operations. It can integrate various video resources including traffic video, platform video, passenger station video, highway video, social security video, vehicle video, etc., to improve the overall video surveillance efficiency, and create more on the basis of video surveillance infrastructure. The application of multiple value-added, so as to achieve the maximum effectiveness of the video surveillance system.
(7) Big data processing technology
The big data preprocessing technology is to further process the data of the access platform according to the specific business rules, including checking the validity of the accessed data, and cleaning the big data. The big data standardization processing technology takes out the cleaned data from the database and converts the data format of the external system into the standard format defined by the platform according to the business rules.
(8) Big Data Fusion Processing Technology
Big data fusion processing technology refers to the use of multi-source traffic information fusion methods, combined with feature fusion technology (identification/classification, neural network, Bayesian network, etc.), target maneuvering information processing technology (adaptive noise model, etc.) and multi-target tracking The information fusion technology improves the robustness and reliability of information systems. Multi-source traffic big data information fusion is divided into three levels: the basic level is the data level fusion, it only completes the data preprocessing and simple correlation; the second level is the feature level fusion, which is based on the characteristics of the existing data to predict the traffic parameters; The third level is state-level integration, which judges the traffic status based on current traffic flow information. The basic process of traffic flow information fusion includes multi-source information extraction, information preprocessing, fusion processing, and target parameter acquisition and state estimation.
(9) Real-time data distribution and subscription technology
Massive traffic big data has the characteristics of large data volume, frequent updates, and high timeliness. It often requires real-time data from other systems to support its business logic. For example, the GPS data of floating vehicles, the current urban road conditions analysis and queuing monitoring analysis of toll stations, the monitoring and analysis system of the provincial Yunzheng satellite positioning network monitoring system, and the operational vehicle safety supervision system need the data shared by the external units.
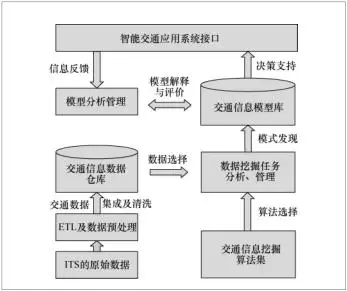
(10) Big Data Mining Technology
Multi-source traffic big data mining is a multi-step process that can be divided into basic stages such as problem definition, data preparation, data analysis, and model evaluation.
Figure 1 Traffic Big Data Mining Model
4 Intelligent Application System of Urban Traffic Big Data
4.1 Traffic Big Data Acquisition Content
Urban traffic big data can be divided into static big data and dynamic big data.
Static traffic big data mainly includes basic spatial data of urban transportation (surface model, high-definition orthophoto, etc.), basic geographic information of cities and surrounding areas (urban road network, intersection layout, implementation information of urban basic traffic), basic information of road traffic network (Road grade, length, and billing information), road passenger transport information (passenger line, passenger ticketing, urban public transport information, station line radiation maps, passenger transportation company information, transportation interchange points, etc.), flight information, train information, Water transport information (ships, starting and ending code points, time of departure, etc.), parking lot information (parking lot location, name, total number of berths, opening and closing status, number of vacant parking spaces, etc.), traffic management information (police area boundary, safety Boundary, police force distribution, traffic posts, law enforcement stations, vehicle management offices, testing sites, examination sites, transit checkpoints, and traffic sampling survey data.
Dynamic traffic Big data come from a wide range of sources and forms, including data obtained through remote sensing such as satellite remote sensing, aerial photogrammetry, low-altitude UAV emergency platforms, ground measurement vehicles, and ground video, and ground intelligence transportation systems, through video and mobile phones. , Bus cards, sensing coils and other sensors and mobile terminals collect data on people, vehicles, roads and other transportation elements. The data that can be collected from people include driving behavior data, payment behavior data, and travel behavior data. The data collected from vehicles include vehicle information data, real-time location data of vehicles, bus operation data, taxi operation data, and crowdsourced traffic data. The road data includes satellite image data, aerial photography data, and road infrastructure data.
4.2 Traffic Big Data Cloud Computing Support Platform
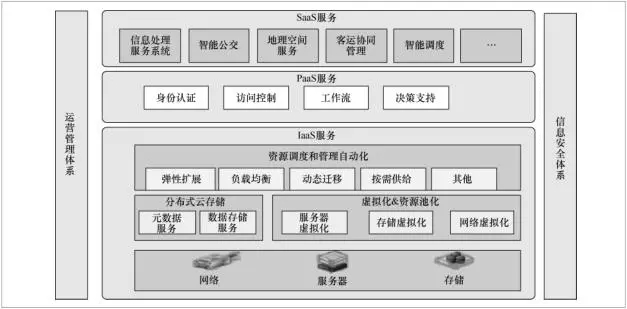
The services of urban traffic big data and related services are implemented using cloud computing technology. The overall logical architecture is shown in Figure 2. Adopt cloud computing technology to support integrated traffic big data, provide self-service management virtual infrastructure on demand and pool them into efficient pools, and provide resources in the form of services. The cloud computing support platform includes data center physical resource management, data center logic resources, data center operation platform and maintenance.
Figure 2 Cloud Computing Support Platform for Urban Traffic Big Data
The urban traffic cloud computing support platform includes multiple subsystems, each providing stable information, management, and monitoring services. In order to support the stable and efficient service of intelligent transportation for 7×24 h, cloud computing virtualization platform can be introduced. Virtualization technology is used to separate the application system from the physical machine, reducing the system interruption service caused by the physical environment, and deleting, upgrading, or changing physical resources without affecting the user.
4.3 Intelligent Application of Traffic Big Data
The smart application system of traffic big data is an intelligent application system based on the traffic big data center and the traffic cloud computing support platform. It adopts the modes of “central data storage and processing†and “local service application†to grasp the massive traffic data. Take real-time data, analyze mining history data, make predictions based on historical data for future situations, and provide decision-making suggestions for intelligent transportation.
The traffic big data intelligent application system can provide intelligent traffic information services for the government, enterprises and the public. The system can provide government departments with traffic administrative supervision and support, mainly providing fine geographic information services, traffic management services, emergency response services, roadside parking supervision services, public transportation supervision services, etc.; for the public to build mobile information services based on mobile applications, through Traffic information services can also collect data on daily travel behaviors of the public, including fine geographic information services, precise real-time road conditions services, precise traffic information services, real-time vehicle information services, traffic guidance information services, parking guidance information services, etc.; Value-added information services include fine geographical information services, bus company vehicle scheduling and auxiliary decision-making, and business data analysis. Different users can share industry data, computing resources, and individualized intelligence analysis results, and have outstanding advantages in data collection and sharing, real-time processing and analysis of large-scale data, and corporate emergencies disposal, which greatly saves system resources and costs. , improve work efficiency.
The technologies used in the system mainly include multi-source heterogeneous traffic information fusion technology based on decision tree-support vector machine (DTM-SVM), basic traffic data service design based on SOA, ZigBee wireless sensor network technology, and mobile internet-based traffic Information application service design, travel time prediction based on machine learning, pedestrian location information service technology based on location services (LBS).
Co-kneader
Melt pump is installed between the main extruder and the die. The benefits of melt pumps for extrusion operations includes the elimination of surging and other fluctuations, reduction of inconsistent melt temperatures, high pressures at lower product temperatures, compensation for the pumping or mixing capacity of the extruder, possibly reduced start-up times, and reduction of energy required by the extruder
Application:
--Color masterbatch/ Concentrates
--High loading filler masterbatch
--Hot-melt adhesive
--Engineering plastics compounding
--Engineered elastomers
|
Model
|
SJW-45(M)
|
SJW-70(M)
|
SJW-100(M)
|
SJW-140(M)
|
|
Screw Diameter (MM)
|
45
|
70
|
100
|
140
|
|
Length Diameter Ratio
|
15-25
|
15-25
|
15-25
|
15-25
|
|
Main Motor Power (KW)
|
15-30
|
55-75
|
90-132
|
160-220
|
|
Max. Screw Speed (RPM)
|
500
|
500
|
500
|
500
|
|
Reference Output (KG/HOUR)
|
40-50
|
150-200
|
300-400
|
800-1000
|