A friend asked, is the network line theory thick? Why is the transmission speed of Category 6 lines faster than Category 5 lines? This is a good question. We usually use more network cables. The various types of network cables are rarely understood. When we do a lot of projects, we all have the illusion that the Super Category 5 line is not much different from the Category 6 line. Today we look at the difference between Category 6 and Category 5.
Comparison of the attributes of Category 1, Category 5 and Category 6
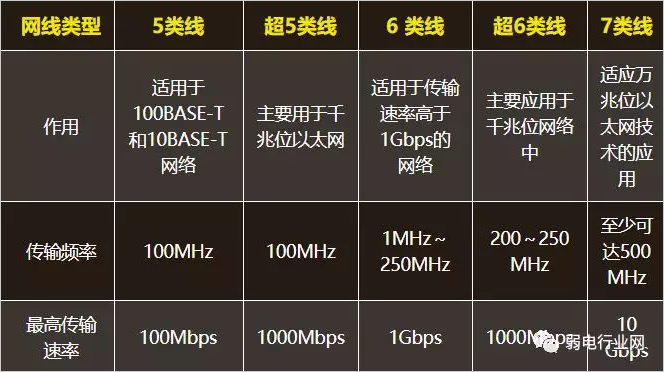
Category 5 line (CAT5): Transmission frequency is 100MHz, used for voice transmission and data transmission with a maximum transmission rate of 100Mbps, mainly used for 100BASE-T and 10BASE-T networks. This is a commonly used Ethernet cable that adds wire density and is a high quality insulating material.
Super Category 5 (CAT5e): Transmission frequency is 100MHz, mainly used for Gigabit Ethernet (1000Mbps). It has small attenuation, less crosstalk, higher attenuation and crosstalk ratio (ACR) and signal-to-noise ratio (Successive Return Loss), and smaller delay error, and the performance is greatly improved.
Category 6 line (CAT6): The transmission frequency is 250MHz, suitable for applications with transmission rates higher than 1Gbps, mainly for Gigabit Ethernet (1000Mbps). The six types of twisted pairs are different in appearance and structure from the five or five types of twisted pairs. They not only increase the insulated cross skeleton, but also place the four pairs of twisted pairs on the cross skeleton. Within the grooves, and the diameter of the cable is also thicker.
Super Category 6 or 6A (CAT6A): The transmission frequency is 200 to 250 MHz, and the maximum transmission speed can reach 1000 Mbps. It is mainly used in Gigabit networks. The Super Category 6 line is an improved version of the Category 6 line, also an unshielded twisted pair cable as specified in ANSI/EIA/TIA-568B.2 and ISO Class 6/E standards for crosstalk, attenuation and signal noise. There is a big improvement over other aspects.
Category 7 (CAT7): The transmission frequency is at least 500 MHz and the transmission rate is up to 10 Gbps. It is mainly used to adapt to the application and development of 10 Gigabit Ethernet technology. This line is a new shielded twisted pair in the ISO 7/F standard.
Second, the difference between Category 5 and Category 6
The difference one: the difference in loss, an important difference between the Category 6 line and the Category 5 network line is to improve the performance in terms of crosstalk and return loss. Home decoration recommends using six types of cable directly.
The difference is two, the thickness of the core is different, the core of the super five types of cable is between 0.45mm and 0.51mm, the core of the six types of cable is between 0.56mm and 0.58mm, and the appearance of the six types of cable is better than the super five. The network cable is much thicker;
The third difference: the line structure is different. The outer skin of the super five types of cable has the "CAT.5e" logo. The six types of cable are obviously "cross skeleton", and the skin is marked by "CAT.6".

Although Category 5 unshielded twisted pair cables can provide transmission bandwidths of up to 1000 Mb/s, they often require the support of expensive special equipment.
"Category 6" refers to Category 6 unshielded twisted pair (CAT6).
The parameters of the six types of unshielded twisted pair cables have been greatly improved, and the bandwidth has also been extended to 250 MHz or higher. The six types of twisted pairs are different in appearance and structure from the five or five types of twisted pairs. They not only increase the insulated cross skeleton, but also place the four pairs of twisted pairs on the cross skeleton. Within the grooves, and the diameter of the cable is also thicker.
The cross skeleton at the center of the cable rotates with the change of the length, and the four pairs of twisted pairs are stuck in the grooves of the skeleton to maintain the relative positions of the four pairs of twisted pairs, thereby improving the balance characteristics of the cable and the crosstalk attenuation. In addition, it is guaranteed that the balanced structure of the cable is not damaged during the installation process. The six types of unshielded twisted pair bare copper wire diameter is 0.57mm (wire gauge is 23AWG), the insulated wire diameter is 1.02mm, and the UTP cable diameter is 6.53mm. Of course, the thicker the better. The signal is stable.
Â
Third, the difference between the super six class line and the seven class line
Super Category 6 line: The maximum transmission frequency is up to 500MHz, which is twice that of Category 6 cable. It is mainly used for 10G (10G) network, and the outer skin is marked with “CAT.6Aâ€. In addition, the Super Category 6 network cable supports 10G Ethernet. There will be a similar logo of 10 Gigabit in appearance;
There are two types of 6 types of wires. Generally, the bare copper wire has a diameter of 23 AWG, which is about 0.573 mm, and has a 24 AWG class 6 wire with a thickness of about 0.511 mm.
Category 7: The performance of Category 7 and Super Category 6 cables is similar. It uses 8 cores of pure copper and has a shielding layer. The performance is more powerful and the transmission rate can reach 10Gbps. It is used in data centers and other occasions.
Each pair has a shielding layer (usually a metal foil shield), and then there is a shielding layer (usually a metal braided screen shielded Braided Shield) with the same interface as the RJ-45. Total shielding (generally metal woven mesh screen shielding) + wire pair shielding (generally metal foil shielding) Category 7 S/FTP Cat.7 (HSYVP-7) Maximum transmission frequency 600MHz, Super Category 7 transmission frequency is 1000MHz Seven categories fully support 10G.

The seven types of wire cores use high-quality oxygen-free copper with a diameter of nearly 0.58mm as the transmission conductor, which is slightly thicker than the Category 6 wire. Chemical foam insulation is used, which greatly improves the transmission capability of a single conductor.
From the core of the network cable, the diameters of the cores of Category 5, Category 6, and Category 7 are increased. The higher the quality of the copper used, the faster the transmission rate and the more stable.
Wine Cup
Xuzhou D.C. International Trading Co., Ltd. , https://www.dcglassbottles.com





